Answer:
Keq = 5.33*10²⁶
Step-by-step explanation:
Based on the standard reduction potential table:
E°(Fe2+/Fe) = -0.45 V
E°(Cu2+/Cu) = +0.34 V
Since the reduction potential of copper is greater than iron, the former acts as the cathode and the latter as anode.
The half reactions are:
Cathode (Reduction):
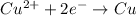
Anode (Oxidation):
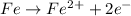
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Overall reaction:
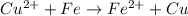
The Gibbs free energy change at 25 C is related to the standard emf (E°) of the cell as well as the equilibrium constant K as:
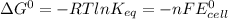
here:
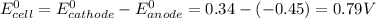
R = 8.314 J/mol-K
T = 25 C = 25+273 = 298 K
n = number of electrons involved = 2
F = 96500 Coulomb/mol e-
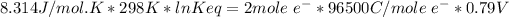
Keq = 5.33*10²⁶