Answer:
2:1
Step-by-step explanation:
The Law of Multiple Proportions states that when two elements A and B combine to form two or more compounds, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratios of small whole numbers.
That is, if one compound has a ratio r₁ and the other has a ratio r₂, the ratio of the ratios r is in small whole numbers.
1. Compound 1
Mass of O = 100.0 - 61.4 = 38.6 g
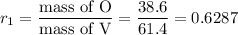
2. Compound 2
Mass of O = 100.0 - 76.1 = 23.9 g
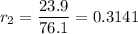
3. Ratio of the ratios
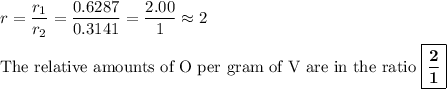
For example. the compounds might be VO₂ and VO.