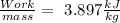Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The work made by the force its equal to the change of mechanical energy
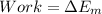
The mechanical energy is given by:
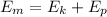
where
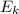 is the kinetic energy and
is the kinetic energy and
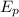 the potential energy.
the potential energy.
We know that, the kinetic energy is
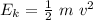
and the potential energy
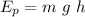
We can put h=0 at Earth's surface, taking this in consideration, the initial Energy is:
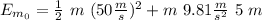
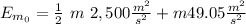
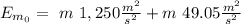
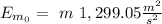
the final Energy is:
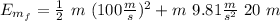
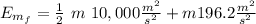
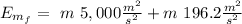
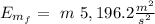
The work will be:
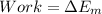
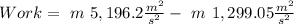
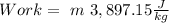
As we don't know the mass, we can take the work over mass: