Answer:
The produced moles are 1,0×10⁻²CO₂.
Step-by-step explanation:
The first thing we should know is what reagent is the limiting one. To know this, it is necessary to obtain moles, thus:
0,020 KMnO₄ liters ×
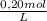 = 4,0×10⁻³ KMnO₄ moles
= 4,0×10⁻³ KMnO₄ moles
0,050 Na₂C₂O₄ liters ×
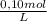 = 5,0×10⁻³ Na₂C₂O₄ moles
= 5,0×10⁻³ Na₂C₂O₄ moles
The global reaction is:
2 MnO₄⁻ (aq) + 5 C₂O₄²⁻ (aq) + 16 H⁺ (aq) → 2 Mn²⁺ (aq) + 10 CO₂ (g) + 8 H₂O
Thus, two moles of MnO₄⁻ reacts with five moles of C₂O₄²⁻. It means that for a complete reaction of 4,0×10⁻³ KMnO₄ moles you need:
4,0×10⁻³ KMnO₄ moles ×
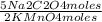 =
=
1,0×10⁻²Na₂C₂O₄ moles but there are just 5,0×10⁻³ Na₂C₂O₄ moles. Thus, limiting reagent is Na₂C₂O₄.
Now, the produced CO₂ moles are calculated with the limiting reagent moles, knowing that 5 C₂O₄⁻ moles produce 10 CO₂ moles, thus:
5,0×10⁻³ Na₂C₂O₄ moles ×
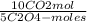 =
=
1,0×10⁻²CO₂ moles
I hope it helps!