Answer: Volume of water to be added is 116 ml.
Step-by-step explanation:
Elevation in boiling point is given by:
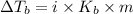
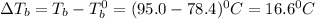 = elevation in boiling point
= elevation in boiling point
i= vant hoff factor = 1 (for non electrolyte)
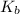 =boiling point constant =
=boiling point constant =
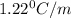
m= molality
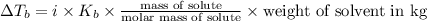
Density of solvent =
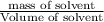
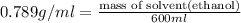
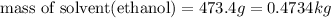 (1kg=1000g)
(1kg=1000g)
Mass of solute (water) = x g
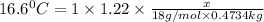
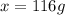
Density of solute =
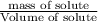
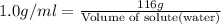
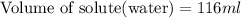
Thus the volume of water to be added is 116 ml.