After the second equilibrium is reached, the moles of
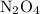 is 6.0 mol.
is 6.0 mol.
How to find pressure?
Initial concentrations:
![\[ [\text{NO}_2]_{\text{initial}} = \frac{35.0 \, \text{mol}}{125.0 \, \text{L}} = 0.28 \, \text{mol/L} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ferhol3srpw3d16s8rfda9hfrrnti1nphb.png)
Equilibrium concentrations after the first reaction:
![\[ [\text{NO}_2]_{\text{equilibrium}} = \frac{8.0 \, \text{mol}}{125.0 \, \text{L}} = 0.064 \, \text{mol/L} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/nk9ads3blis6pbdojfdc1i8qopzu88vqdy.png)
Change in moles of
 during the first reaction:
during the first reaction:
![\[ \text{Change} = 35.0 \, \text{mol} - 8.0 \, \text{mol} = 27.0 \, \text{mol} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/tfrksyu3hk6g8qi6w8axn9k191jg7s114a.png)
Calculate Q after the first reaction:
![\[ Q = (0)/((0.064)^2) = 0 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yvhthoh1wxjouygp0eq7xh57zhgv9gixm9.png)
Since Q < K, the reaction proceeds to the right (formation of more
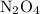 ).
).
Change in moles of
 due to the addition of 12.0 mol:
due to the addition of 12.0 mol:
![\[ \text{Change} = +12.0 \, \text{mol} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/nbnf7f5binyo8j3mwxsblcovbyrj6xydes.png)
New equilibrium concentration of
 :
:
![\[ [\text{NO}_2]_{\text{equilibrium, new}} = 0.064 \, \text{mol/L} + \frac{12.0 \, \text{mol}}{125.0 \, \text{L}} = 0.160 \, \text{mol/L} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/k7i8vgo7eizwpxmod3xrwjzppdr27gm1qz.png)
Calculate the new equilibrium concentration of
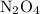 :
:
![\[ [\text{N}_2\text{O}_4]_{\text{equilibrium, new}} = \frac{\text{Change in moles of } \text{NO}_2}{2} = \frac{12.0 \, \text{mol}}{2} = 6.0 \, \text{mol} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/frjs302sp97ws8utogewzp5z42ylw6yt5e.png)
Therefore, after the second equilibrium is reached, the moles of
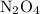 is 6.0 mol.
is 6.0 mol.
Complete question:
Nitrogen dioxide is one of the many oxides of nitrogen (often collectively called "NOx") that are of interest to atmospheric chemistry. It can react with itself to form another form of NOx, dinitrogen tetroxide. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 125.L tank with 35.mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. When the mixture has come to equilibrium she determines that it contains 8.0mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. The engineer then adds another 12.mol of nitrogen dioxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of dinitrogen tetroxide after equilibrium is reached the second time.