Answer:
The rate of descomposition of N₂O₅ is: 2,8 M/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The global reaction is:
2 N₂O₅ (g) → 4 NO₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
The problem says that rate of formation of NO₂ = 5,5x10⁻⁴ M/s where M is molarity -
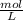 -
-
The rate of descomposition of N₂O₅ is:
5,5x10⁻⁴
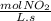 ×
×
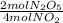 = 2,8 M/s
= 2,8 M/s
I hope it helps!