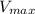Answer:
a)0.0229 m
b)0.393 rad
c)1.57
d)707.6 N
e)0.298 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
- Mass of the machine, m=70 kg
- Stiffness of the system, k=30000 N/m
- Damping ratio=0.2
- Damping force, F=450 N
- Angular velocity

a)We know that the amplitude X at steady state is given by

Where
![X=((450)/(70))/(√(20.7^2-13^2)^2 +(2* 0.2*20.7*13)^2))\\[tex]X=0.0229\ \rm m](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/zgvwp57c6ufu445mfiyphsj6yae28llp5n.png)
b) The phase shift of the motion is given by

c)Transmissibility ratio is given by

d)The magnitude of the force transmitted to the ground is

e)The maximum velocity is given by