Answer:
33.57μC
Step-by-step explanation:
The moving particle will execute a circular motion when the Electric force between the particles is equal to the centripetal force necessary for the circular motion at a velocity equal to 74m/s and a radius = 0.246m. You can find the value for the centripetal force with this expression:
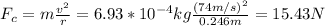
Now, this is the value that the electric force between the charges should be. The electric force is given by this expresion:
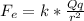
k is the Coulomb constant, equal to 9*10^9 Nm^2/C^2. Then:

Or 33.57μC