Answer:
The pH is 7.0
Step-by-step explanation:
The equilibrium relevant for the problem is:
H₂PO4⁻ ⇌ HPO4⁻² + H⁺ pKa = 6.86
The Henderson-Hasselbalch (H-H) equation describes the pH of a buffer solution, using the concentrations of the acid and its conjugate base:
![pH=pka+log([A^(-) ])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/buanvnmw63rak1rwruil6owlh2k1c4la5k.png)
For this case, [A⁻] = [HPO4⁻²], and [HA] = [H₂PO4⁻]. Thus:
![pH=pka+log([HPO4^(-2) ])/([H2PO4^(-) ])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/l0six4dqvyjxxg61fbedej2ss1h8q00htb.png)
We put the concentrations and pka given in the problem in the H-H equation:
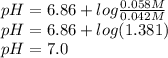
P.S.: The actual pka for the equilibrium is 7.21, according to literature. Not 6.86 like the problem says. If we use a pka of 7.21 then the pH would be 7.35.