Answer:
Explanation:-
Osmotic pressure is a colligative property which depends on the amount of solute added.

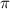 = osmotic pressure = 5.1 atm
= osmotic pressure = 5.1 atm
C= concentration in Molarity
R= solution constant = 0.0821 Latm/Kmol
T= temperature = 312 K
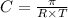
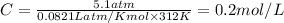
Thus the equation for calculating the molarity of this solution is