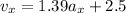Answer:
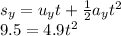
and,
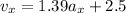
Explanation:
In the question,
Taking the elevation of pool along the y-axis, and length of the board along the x-axis.
On drawing the illustration in the co-ordinate system we get,
lₓ = 2 m
uₓ = 2.5 m/s
and,
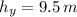
So,
From the equations of the laws of motion we can state that,
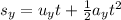
So,
On putting the values we can say that,
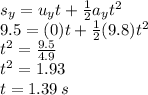
Now,
The equation of the motion in the horizontal can be given by,
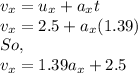
Therefore, the equations of the motions in the horizontal and verticals are,
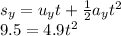
and,