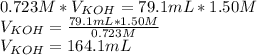Answer:
The volume of the potassium hydroxide solution was 164.1 mL
Step-by-step explanation:
In the equivalence point of a titration between an acid an a base, the moles of H⁺ are equal to the moles of OH⁻.
In the case of potassium hydroxide (KOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl), an equation that represents the equivalence point would be:
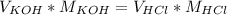
Using that equation and the data given in the problem, we can calculate the volume of potassium hydroxide: