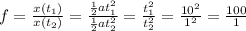Answer:
1) d
2) 5 m/s
3) 100
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation of position x for a constant acceleration a and an initial velocity v₀, initial position x₀, time t is:
(i)
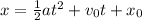
The equation for velocity v and a constant acceleration a is:
(ii)
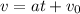
1) Solve equation (ii) for acceleration a and plug the result in equation (i)
(iii)
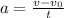
(iv)
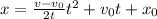
Simplify equation (iv) and use the given values v = 0, x₀ = 0:
(v)
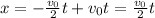
2) Given v₀= 3m/s, a=0.2m/s², t=10 s. Using equation (ii) to get the final velocity v:
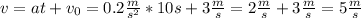
3) Given v₀=0m/s, t₁=10s, t₂=1s and x₀=0. Looking for factor f = x(t₁)/x(t₂) using equation(i) to calculate x(t₁) and x(t₂):