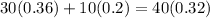If
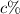 is the unknown concentration of the second solution, then each mL of this solution that is used in the new one contributes
is the unknown concentration of the second solution, then each mL of this solution that is used in the new one contributes
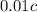 mL of acid.
mL of acid.
There are 40 mL of the new solution, and one quarter is made up of 20% acid while the remaining three-quarters is made up of the
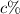 solution - that is, 10 mL of a 20% acid solution are used, so that its contribution is 0.2(10 mL) = 2 mL of acid, while 30 mL of the
solution - that is, 10 mL of a 20% acid solution are used, so that its contribution is 0.2(10 mL) = 2 mL of acid, while 30 mL of the
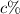 solution are used, so it contributes
solution are used, so it contributes
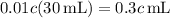 of acid.
of acid.
In this new solution, we want to get a concentration of 32% acid, so it should contain 0.32(40 mL) = 12.8 mL of acid. Then the total amount of acid in the new solution satisfies
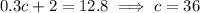
so the second solution has a concentration of 36%. The equation used here is the same as the first choice (a),