Answer:
74.8g
Step-by-step explanation:
Given parameters:
Mass of carbon = 20.4g
Mass of oxygen = 69.0g
Mass of excess oxygen = 14.6g
Unknown:
Mass of carbon dioxide produced = ?
Solution
The equation of the reaction is shown below:
C + O₂ → CO₂
From the statement of the problem, we can see that the oxygen gas is in excess of the carbon burning. This implies that the extent of the reaction would be determined by how much carbon is there to burn. The carbon is called the limiting reagent. The reagent whose quantity is in short supply.
It is the limiting reagent that can precisely give us the amount of carbon dioxide that would be produced.
From the given parameters, we would simply evaluate the number of moles of the carbon using the expression below:
Number of moles of carbon =
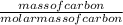
molar mass of carbon is 12g/mol
Number of moles of carbon =
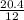 = 1.7moles
= 1.7moles
From the reaction:
1 mole of Carbon reacted with oxygen to produce 1 mole carbon dioxide
1.7moles of carbon will also produce 1.7 mole of carbon dioxide
Therefore:
mass of carbon dioxide= number of moles x molar mass
Molar mass of carbon dioxide = 12 + (2x16) = 44g/mol
Mass of carbon dioxide = 1.7 x 44 = 74.8g