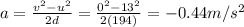Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all, we need to calculate the distance covered by the locomotive during the reaction time, which is
t = 0.46 s
During this time, the locomotive travels at
v = 13 m/s
And the motion is uniform, so the distance covered is
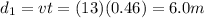
The locomotive was initially 200 m from the crossing, so the distance left to stop is now
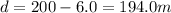
And now the locomotive has to slow down to a final velocity of
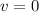 in this distance. We can find the minimum deceleration needed by using the suvat equation:
in this distance. We can find the minimum deceleration needed by using the suvat equation:
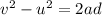
where
v = 0 is the final velocity
u = 13 m/s is the initial velocity
a is the deceleration
d = 194.0 m is the distance to stop
Solving for a,