Answer:
(a)
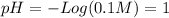
(b)
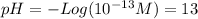
(c)
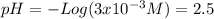
(d)
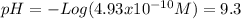
(e)
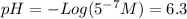
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate de pH of an acid solution the formula is:
![pH = -Log ([H^(+)]) = 1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/p7ebyc5uceinyxjnc9d52y05xntte9ld18.png)
were [H^{+}] is the concentration of protons of the solution. Therefore it is necessary to know the concentration of the protons for every solution in order to solve the problem.
(a) and (c) are strong acids so they dissociate completely in aqueous solution. Thus, the concentration of the acid is the same as the protons.
(b) and (e) are strong bases so they dissociate completely in aqueous solution too. Thus, the concentration of the base is the same as the oxydriles. But in this case it is necessary to consider the water autoionization to calculate the protons concentration:
![K_(w) =[H^(+) ][OH^(-)]=10^(-14)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/xtnf0gn18rehlak9tcxr5t7tr5p1kukt9d.png)
clearing the
![[H^(+) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/gpdg8hk17mz7lvtewh22u5nmrlg1fyk1sq.png)
![[H^(+) ]=(10^(-14))/([OH^(-)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/e6cf7mmtm48f3bz5wv5pxa7fdbx193dd1r.png)
(d) is a weak base so it is necessary to solve the equilibrium first, knowing
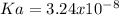
The reaction is
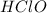 →
→
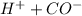 so the equilibrium is
so the equilibrium is
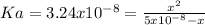
clearing the x
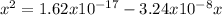
![x=[H^(+)]=4.93x10^(-10)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/dd5u1evxnq71izl7pk0qq1zvvk44elsabq.png)