Step-by-step explanation:
a) Dark matter: a kind of matter we can't directly observe but that we can imply its presence in various observations including gravitational effects which can't be explained by accepting theories of gravity unless more matter is present. This is the reason why dark matter is thought to account for around 80% of the matter in the universe.
b)21cm Radiation: also called hydrogen line, is a spectral line emitted by neutral hydrogen, it has a frequency of 1420megahertz and 21 cm wavelength. In astronomy, this line is used to study the amount and velocity of hydrogen in the galaxy.
Milky way: it's a barred spiral galaxy with more than 200 billion stars, approximately 100000 light-years in diameter and the sun is located about 28000light years from the center.
From the outside its structure has the following characteristics:
- Galactic disk: it is made out of old and young stars, as well as gas and dust, gravitational interactions between stars cause a circular motion with up and down motions, this disk is divided in three other parts, a nucleus (the center of the disk), a bulge (around the nucleus) and spiral arms (extended areas)
- Globular clusters: located above and below the disk, the stars in this zone are older and there's no gar or dust.
- Halo: large region surrounding the galaxy, it is made of hot gas and dark matter.
Two fundamentals parameters of the milky Way are
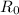 (the radial distance from de sun to the galactic center) and
(the radial distance from de sun to the galactic center) and
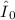 , the galactic rotational velocity at
, the galactic rotational velocity at
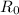
Einstein's Theory of General Relativity: general relativity is a metric theory of gravitation, that defies gravity as a geometric property of space and time, this means there's no gravitational force deflecting objects from their natural straight paths, but a change in properties of space and time that changes this straight path into a curve.
At weak gravitational fields and slow speed, this theory overlaps with Newton's.
Pulsars: they are rotating neutron stars that emit a focused beam of electromagnetic radiation its formation happens when a medium mass star dies and it maintains its angular momentum emitting a powerful blast of radiation along its magnetic field lines. They are useful to search for gravitational waves, and even to find extrasolar planets.
I hope you find this information interesting and useful! Good luck!