Answer:
Statement (a) is true
Step-by-step explanation:
- Conjugate base of an acid is formed from deprotonation of corresponding acid.
- For an example, consider an acid e.g.
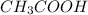 (acetic acid)
(acetic acid) - Acid-base equilibrium for acetic acid in aqueous solution is represented as:
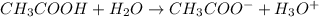
- Here
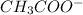 (acetate ion) is the conjugate base of acetic acid.
(acetate ion) is the conjugate base of acetic acid. - So, clearly, acetic acid has one more proton as compared to acetate ion
Hence statement (a) is true