Answer:
The heat released is 56.7 kJ.
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve this problem, first we need to find out the standard enthalpy of reaction, that is, the energy released at constant pressure in standard conditions (P=1bar, T=298.15K). We can find it using the expression:
ΔH°r = Σn(p).ΔH°f(p) - Σn(r).ΔH°f(r)
where,
n refers to the number of moles of reactants and products in the balanced equation
ΔH°f refers to standard enthalpies of formation (which can be found in tables).
Given the equation:
2 H₂O₂(l) → 2 H₂O(g) + O₂(g)
We can replace with the proper data in the equation:
ΔH°r = Σn(p).ΔH°f(p) - Σn(r).ΔH°f(r)
ΔH°r= [2 mol . ΔH°f H₂O(g) + 1 mol . ΔH°f O₂(g)] - [2 mol . ΔH°f H₂O₂(l)]
ΔH°r= [2 mol . (-241.8 kJ/mol) + 1 mol . 0 kJ/mol] - [2 mol . (-187.8 kJ/mol)]
ΔH°r = -108.0 kJ
Since enthalpy is an extensive property, it depends on the amount of reagents. In this case, 108.0 kJ of heat are released every 2 moles of H₂O₂(l) decomposed. Then, for 1.05 mol of H₂O₂(l):
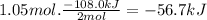
By convention, the negative sign means that heat is released.