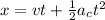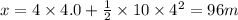Answer:
(a) d = 20 m
(b) d' = 80 m
(c) x = 28 m
(d) x' = 96 m
Solution:
As per the question:
Initial velocity of the object, v = 0
Constant acceleration of the object,
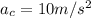
(a) Distance traveled, d in t = 2.0 s is given by the second eqn of motion:
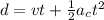
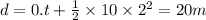
(b) Distance traveled, d' in t = 4.0 s is given by the second eqn of motion:
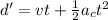
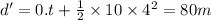
Now, when initial velocity, v = 4 m/s, then
(c) Distance traveled, x in t = 2.0 s is given by the second eqn of motion:
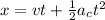
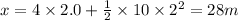
(d) Distance traveled, x' in t = 4.0 s is given by the second eqn of motion: