Answer:
pH = 5,22
Step-by-step explanation:
A buffer consist in a solution with both conjugate acid (HA) and conjugate base (A⁻). To know the concentration of both A⁻ and HA you use Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
pH = pka + log₁₀
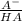
In the problem:
5,23 = 5,14 + log₁₀
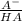
1,23 =
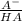 (1)
(1)
Also, you know buffer concentration is 1,0 M:
1,0 M = A⁻ + HA (2)
Replacing (2) in (1):
HA = 0,45 M, thus:
A⁻ = 0,55 M.
The addition of 1.50 mL of 5.00 M HCl represents a concentration of:
1,50x10⁻³ L×
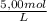 ÷ 0,5 L = 0,015 M of HCl
÷ 0,5 L = 0,015 M of HCl
The buffer equilibrium is:
HA ⇄ A⁻ + H⁺ ka =
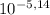
The concentrations in equilibrium are:
[HA] = 0,45 M + x
[A⁻] = 0,55 M - x
[H⁺] = 0,015 M -x
Because the equilibrium is displaced to the left.
The equation of equilibrium is:
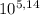 =
=
![([0,015M -x][0,55M-x])/([0,45M-x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/aph5zt7oivx87f0nhcu28lryznjiad9x8v.png)
You will obtain:
x² - 0,565x + 8,24674x10⁻³ = 0
Solving:
x = 0,5500061 ⇒ No physical sense
x = 0,01499391
Thus, [H⁺] = 0,015 - 0,01499391 = 6,09x10⁻⁶
As pH = -log₁₀ [H⁺]
pH = 5,22
I hope it helps!