Answer: The mass of solid NaOH required is 80 g
Step-by-step explanation:
Equivalent weight is calculated by dividing the molecular weight by n factor. The equation used is:
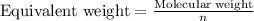
where,
n = acidity for bases = 1 (For NaOH)
Molar mass of NaOH = 40 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
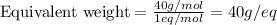
Normality is defined as the umber of gram equivalents dissolved per liter of the solution.
Mathematically,
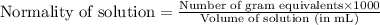
Or,
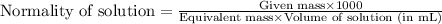 ......(1)
......(1)
We are given:
Given mass of NaOH = ?
Equivalent mass of NaOH = 40 g/eq
Volume of solution = 400 mL
Normality of solution = 5 eq/L
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
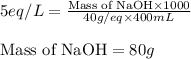
Hence, the mass of solid NaOH required is 80 g