Answer:
11.39
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
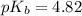
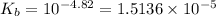
Given that:
Mass = 1.805 g
Molar mass = 82.0343 g/mol
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
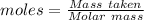
Thus,
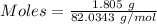
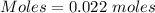
Given Volume = 55 mL = 0.055 L ( 1 mL = 0.001 L)
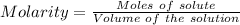
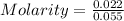
Concentration = 0.4 M
Consider the ICE take for the dissociation of the base as:
B + H₂O ⇄ BH⁺ + OH⁻
At t=0 0.4 - -
At t =equilibrium (0.4-x) x x
The expression for dissociation constant is:
![K_(b)=\frac {\left [ BH^(+) \right ]\left [ {OH}^- \right ]}{[B]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6ctjsulxcobg3ekia7jkacqhhm25r4bjsp.png)
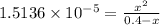
x is very small, so (0.4 - x) ≅ 0.4
Solving for x, we get:
x = 2.4606×10⁻³ M
pOH = -log[OH⁻] = -log(2.4606×10⁻³) = 2.61
pH = 14 - pOH = 14 - 2.61 = 11.39