Step-by-step explanation:
According to the Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base theory:
- An acid is defined as a substance which looses donates protons and thus forming conjugate base
- A base is defined as a substance which accepts protons and thus forming conjugate acid.
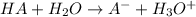
Suppose acid Ha is getting dissociated in its solution and after dissociation it donates its proton to water molecule and forms conjugate base. Where as water (acting as a base) accepts protons and forms conjugate acid.
HA = Acid
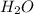 = Base
= Base
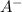 = Conjugate base
= Conjugate base
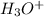 = Conjugate acid
= Conjugate acid
For example:
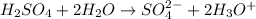
Sulfuric acid dissociating in its solution to form conjugate base and conjugate acid.
Sulfuric acid = Acid
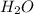 = Base
= Base
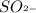 = Conjugate base
= Conjugate base
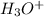 = Conjugate acid
= Conjugate acid