Answer:
a) 0,857 g of H₃PO₄ with 9,016 g of KH₂PO₄
b) 166 mL of 0,400M NaOH
c) 22 mL of 0,400M HCl
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The appropriate weak acid and conjugate salt are:
H₃PO₄ ⇄ H₂PO₄⁻ + H⁺ where pka = 2,12
Henderson–Hasselbalch equation finding pH = 3:
3 = 2,12 + log₁₀
![([H2PO4-])/([H3PO4])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ayv2e1p18v98k0aexi5n7t2m96y38kktrs.png)
7,59 =
![([H2PO4-])/([H3PO4])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ayv2e1p18v98k0aexi5n7t2m96y38kktrs.png) (1)
(1)
If buffer concentration is 0,300M:
0,300 M = [H₃PO₄] + [H₂PO₄⁻] (2)
Replacing (2) in (1):
[H₃PO₄] = 0,035 M
Thus:
[H₂PO₄⁻] = 0,265 M
Thus, to prepare this buffer you need weight:
0,035 M × 0,250 L = 8,75x10⁻³ moles ×
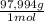 = 0,857 g of H₃PO₄
= 0,857 g of H₃PO₄
And:
0,265 M × 0,250 L = 6,63x10⁻² moles ×
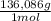 = 9,016 g of KH₂PO₄
= 9,016 g of KH₂PO₄
b) Using 0,400 M NaOH the equilibrium is:
H₃PO₄ + NaOH ⇄ H₂PO₄⁻ + H₂O
Knowing the equilibrium concentrations are:
[H₃PO₄] = 0,035 M = 0,300 M - x -Because in the first all 0,300 M must be of H₃PO₄-
[H₂PO₄⁻] = 0,265 M
Thus, x = 0,265 M are NaOH needed to obtain the desire pH. Those are obtained thus:
0,265 mol/ L × 0,250L ×
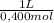 = 0,166 L ≡ 166 mL of 0,400M NaOH
= 0,166 L ≡ 166 mL of 0,400M NaOH
c) Using 0,400 M HCl the equilibrium is:
H₃PO₄ ⇄ H₂PO₄⁻ + HCl
Knowing the equilibrium concentrations are:
[H₃PO₄] = 0,035 M
[H₂PO₄⁻] = 0,265 M = 0,300 M - x -Because in the first all 0,300 M must be of H₂PO₄-
Thus, x = 0,035 M are HCl needed to obtain the desire pH. Those are obtained thus:
0,035 mol/ L × 0,250L ×
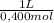 = 0,022 L ≡ 22 mL of 0,400M HCl
= 0,022 L ≡ 22 mL of 0,400M HCl
I hope it helps!