Answer: The new pH of resulting solution is 6.03
Step-by-step explanation:
We are adding hydrochloric acid to the solution, so it will react with salt (sodium hydrogen carbonate) only.
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
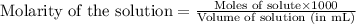
Molarity of hydrochloric acid = 0.15 M
Volume of solution = 3 mL
Putting values in above equation, we get:
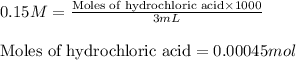
- For sodium hydrogen carbonate:
Molarity of sodium hydrogen carbonate = 0.025 M
Volume of solution = 150 mL
Putting values in above equation, we get:
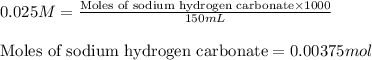
Molarity of carbonic acid = 0.045 M
Volume of solution = 150 mL
Putting values in above equation, we get:
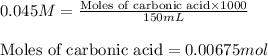
The chemical reaction for sodium hydrogen carbonate and hydrochloric acid follows the equation:

Initial: 0.00375 0.00045 0.00675
Final: 0.00330 - 0.00720
Volume of solution = 150 + 3 = 153 mL = 0.153 L (Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
To calculate the pH of acidic buffer, we use the equation given by Henderson Hasselbalch:
![pH=pK_a+\log(([salt])/([acid]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wwf6o5cvurukvvigp9qetx7pcmu718wast.png)
![pH=pK_a+\log(([NaHCO_3])/([H_2CO_3]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/29vwhwwbe2r63j6jathsrwblwmp3ezffau.png)
We are given:
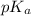 = negative logarithm of acid dissociation constant of carbonic acid = 6.37
= negative logarithm of acid dissociation constant of carbonic acid = 6.37
![[NaHCO_3]=(0.0033)/(0.153)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/uu3pjgr59z95lvjawxig7vjeo9bfoq5fsa.png)
![[H_2CO_3]=(0.0072)/(0.153)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qwk0sr75e5szjhmm1pk5bvqiwyg32tjq53.png)
pH = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
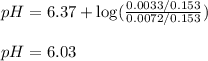
Hence, the new pH of the solution is 6.03