Answer:
absolute pressure = 1.07 lbft/in^2
Step-by-step explanation:
given data:
vaccum gauge reading h = 27.86 inch = 2.32 ft
we know that
gauge pressure p is given as
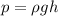
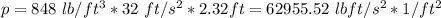
we know that
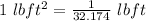
1 ft = 12 inch
therefore
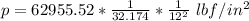
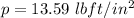
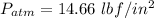
so absolute pressure =
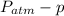
= 14.66 - 13.59 = 1.07 lbft/in^2