Answer:
The rate constant at T = 100 C is 1.0*10⁻³
Step-by-step explanation:
The Arrhenius equation relates two rate constants K1 and K2 measured at temperatures T1 and T2 as shown below:
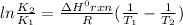
here, ΔHrxn = standard enthalpy change of the reaction
R = gas constant
From the given information:
K1 = 7.4*10^-4
T1 = 25 C = 25+273 = 298 K
T2 = 100 C = 100+273 = 373K
ΔH°=4.1kJ/mol
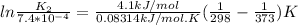
K2 = 1.03*10⁻³