Answer : The value of
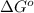 for the reaction is -959.1 kJ
for the reaction is -959.1 kJ
Explanation :
The given balanced chemical reaction is,
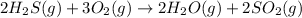
First we have to calculate the enthalpy of reaction
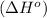 .
.
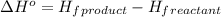
![\Delta H^o=[n_(H_2O)* \Delta H_f^0_((H_2O))+n_(SO_2)* \Delta H_f^0_((SO_2))]-[n_(H_2S)* \Delta H_f^0_((H_2S))+n_(O_2)* \Delta H_f^0_((O_2))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/j7d182tsmv92v0mnqec2ni7qg9fyrblum9.png)
where,
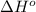 = enthalpy of reaction = ?
= enthalpy of reaction = ?
n = number of moles
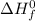 = standard enthalpy of formation
= standard enthalpy of formation
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get:
![\Delta H^o=[2mole* (-242kJ/mol)+2mole* (-296.8kJ/mol)}]-[2mole* (-21kJ/mol)+3mole* (0kJ/mol)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1zzo0qoe6lds90r1fa1o2xra34dedbuob3.png)
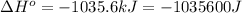
conversion used : (1 kJ = 1000 J)
Now we have to calculate the entropy of reaction
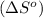 .
.
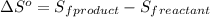
![\Delta S^o=[n_(H_2O)* \Delta S_f^0_((H_2O))+n_(SO_2)* \Delta S_f^0_((SO_2))]-[n_(H_2S)* \Delta S_f^0_((H_2S))+n_(O_2)* \Delta S_f^0_((O_2))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pltiu162qu2vsmsncja1gpb4n3w9pfvu03.png)
where,
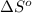 = entropy of reaction = ?
= entropy of reaction = ?
n = number of moles
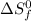 = standard entropy of formation
= standard entropy of formation
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get:
![\Delta S^o=[2mole* (189J/K.mol)+2mole* (248J/K.mol)}]-[2mole* (206J/K.mol)+3mole* (205J/K.mol)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yv1quzf48xr4cqoe5v41eq80esilznpnf1.png)
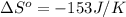
Now we have to calculate the Gibbs free energy of reaction
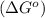 .
.
As we know that,
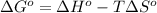
At room temperature, the temperature is 500 K.
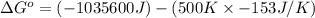
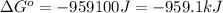
Therefore, the value of
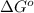 for the reaction is -959.1 kJ
for the reaction is -959.1 kJ