Answer:
- 0th:
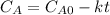
- 1st:
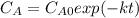
- 2nd:
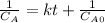
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
For the ideal reaction A→B:
- Zeroth order rate law: in this case, we assume that the concentration of the reactants is not included in the rate law, therefore the integrated rate law is:
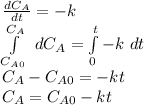
- First order rate law: in this case, we assume that the concentration of the reactant is included lineally in the rate law, therefore the integrated rate law is:
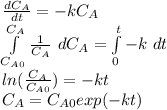
- Second order rate law: in this case, we assume that the concentration of the reactant is squared in the rate law, therefore the integrated rate law is
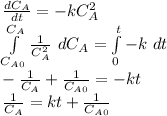
Best regards.