Answer: 14.2 grams
Explanation:-
According to avogadro's law, 1 mole of every substance occupies 22.4 L at STP and contains avogadro's number
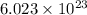 of particles.
of particles.
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
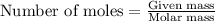
given mass of phosphorous (P) = 3.07 g
Molar mass of phosphorous (P) = 31 g/mol
Putting in the values we get:
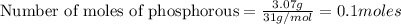
given mass of oxygen
 = 6.09 g
= 6.09 g
Molar mass of oxygen
 = 32 g/mol
= 32 g/mol
Putting in the values we get:
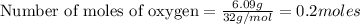
According to stoichiometry:
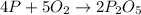
4 moles of phosphorous combine with 5 moles of oxygen
Thus 0.1 moles of phosphorous combine with =
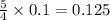 moles of oxygen
moles of oxygen
Thus phosphorous acts as limiting reagent as it limits the formation of product and oxygen is the excess reagent.
4 moles of phosphorous gives= 2 moles of
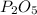
Thus 0.1 moles of phosphorous gives =
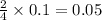 moles of
moles of
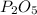
mass of
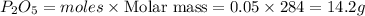
Thus the theoretical yield of
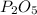 is 14.2 grams.
is 14.2 grams.