Answer:
The solution of the system of linear equations is
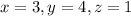
Explanation:
We have the system of linear equations:
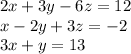
Gauss-Jordan elimination method is the process of performing row operations to transform any matrix into reduced row-echelon form.
The first step is to transform the system of linear equations into the matrix form. A system of linear equations can be represented in matrix form (Ax=b) using a coefficient matrix (A), a variable matrix (x), and a constant matrix(b).
From the system of linear equations that we have, the coefficient matrix is
![\left[\begin{array}{ccc}2&3&-6\\1&-2&3\\3&1&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/yle4lz6cdfd6pelm7xsu4aep5m0sson2dn.png)
the variable matrix is
![\left[\begin{array}{c}x&y&z\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/uu6s9zqhmjue2omk8zafbiya4xzriiuok7.png)
and the constant matrix is
![\left[\begin{array}{c}12&-2&13\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/tb07dz04tv3uo9o9zpz0drawn8xeof1vgp.png)
We also need the augmented matrix, this matrix is the result of joining the columns of the coefficient matrix and the constant matrix divided by a vertical bar, so
![\left[\begin{array}c2&3&-6&12\\1&-2&3&-2\\3&1&0&13\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/irgga1ub75cnaw3qhrljditc0sf21jcy87.png)
To transform the augmented matrix to reduced row-echelon form we need to follow these row operations:
- multiply the 1st row by 1/2
![\left[\begin{array}c1&3/2&-3&6\\1&-2&3&-2\\3&1&0&13\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/3bpk8g2m38w7i304jkxmtofgl00kfrxota.png)
- add -1 times the 1st row to the 2nd row
![\left[\begin{array}ccc1&3/2&-3&6\\0&-7/2&6&-8\\3&1&0&13\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/hgjel1l9mwjohpw00jbbl1rxz4qusgzvr2.png)
- add -3 times the 1st row to the 3rd row
![\left[\begin{array}c1&3/2&-3&6\\0&-7/2&6&-8\\0&-7/2&9&-5\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/1uoevgczdln37rr7g1skr33g829nohpcb2.png)
- multiply the 2nd row by -2/7
![\left[\begin{array}c1&3/2&-3&6\\0&1&-12/7&16/7\\0&-7/2&9&-5\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/1e5ugn0wmij629z4zno737u85craq6lvaz.png)
- add 7/2 times the 2nd row to the 3rd row
![\left[\begin{array}c1&3/2&-3&6\\0&1&-12/7&16/7\\0&0&3&3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/ur50gtqd3br31ez0xz4zocomwcdwmqzotv.png)
- multiply the 3rd row by 1/3
![\left[\begin{array}ccc1&3/2&-3&6\\0&1&-12/7&16/7\\0&0&1&1\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/1e9lnygwrpchhw5l1srhhfgi0tlnid28lt.png)
- add 12/7 times the 3rd row to the 2nd row
![\left[\begin{array}ccc1&3/2&-3&6\\0&1&0&4\\0&0&1&1\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/vkff0g1z7b5e8e0q5rmsmf8q986gs3ujq5.png)
- add 3 times the 3rd row to the 1st row
![\left[\begin{array}ccc1&3/2&0&9\\0&1&0&4\\0&0&1&1\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/k2ranc0je7b6x7tehlao69uk6sn6er5tvw.png)
- add -3/2 times the 2nd row to the 1st row
![\left[\begin{array}ccc1&0&0&3\\0&1&0&4\\0&0&1&1\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/1nyzudn2xxrnyouo6j7l7hjmgdluc7m3xh.png)
From the reduced row echelon form we have that
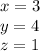
Since every column in the coefficient part of the matrix has a leading entry that means our system has a unique solution.