Answer:
(a) 62.57 L
(b) 801.94 kPa
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
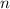 = number of moles of gas = 10.3 mol
= number of moles of gas = 10.3 mol
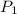 = initial pressure of the gas =
= initial pressure of the gas =
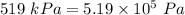
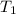 = initial temperature of the gas =
= initial temperature of the gas =
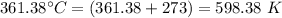
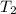 = final temperature of the gas =
= final temperature of the gas =
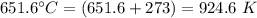
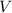 = volume of the tank
= volume of the tank
R = universal gas constant =
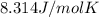
Part (a):
Using Ideal gas equation, we have
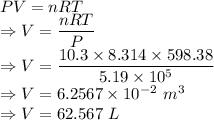
Hence, the volume of the container is 62.567 L.
Part (b):
As the volume of the container remains constant.
Again using ideal gas equation,
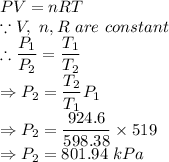
Hence, the final pressure of the gas is now 801.94 kPa.