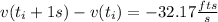Answer:
- 32.17 fts/s in the imperial system, -9.8 m/s in the SI
Step-by-step explanation:
We know that acceleration its the derivative of velocity with respect to time, this is (in 1D):
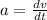
So, if we wanna know the change in velocity, we can take the integral:
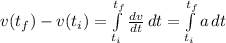
Luckily for us, the acceleration in this problem is constant
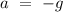
the minus sign its necessary, as downward direction is negative. Now, for a interval of 1 second, we got:
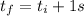
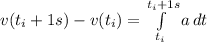
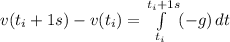
![v(t_i + 1 s) - v(t_i) = [-g t]^(t_i + 1 s)_(t_i)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/rn4ckjrbjme6lqxc1izrzg973dtkbrhyvz.png)
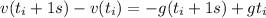
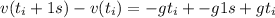
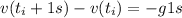
taking g in the SI
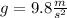
this is:
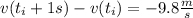
or, in imperial units:
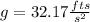
this is: