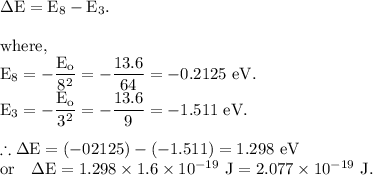Answer:
(a):
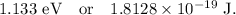
(b):
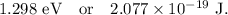
Step-by-step explanation:
The energy of the photon that absorbed by a hydrogen atom causes a transition is equal to the difference in energy levels of the hydrogen atom corresponding to that transition.
According to Rydberg's formula, the energy corresponding to
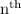 level in hydrogen atom is given by
level in hydrogen atom is given by
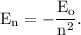
where,
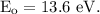
Part (a): For the electronic transition from the n = 3 state to the n = 6 state.
The energy of the photon which cause this transition is given by
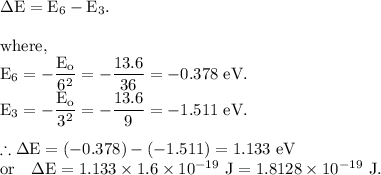
Part (b): For the electronic transition from the n = 3 state to the n = 8 state.
The energy of the photon which cause this transition is given by