Answer:
802.11g:
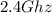
802.11a:
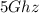
802.11n:
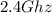 and
and
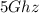
802.11ac:
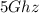
Step-by-step explanation:
802 is a Wi-Fi standard established by the IEEE in which, according to the corresponding standard, a data transmission rate is related.
About some of those standars:
802.11a: works with connections up to 54Mbps, operates in the 5GHz band,
802.11b: Works with connections up to 11mbps, operates in the 2.4GHz band,
802.11g: works with connections up to 54mbps, operates in the 2.4GHz band,
802.11n: Works with connections up to 600mbps, operates in the 2.4GHz and 5GHz band,
802.11ac: works with connections up to 1300Mbps, operates in the 5GHz band,