Answer:
The polynomial equation that passes through the points is
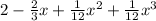
Explanation:
Suppose you have a function y = f(x) which goes through these points
A(-5,-3), B(-2,3). C(3,3), D(6,19)
there is a polynomial P(x) of degree 3 which goes through these point.
We use the fact that four distinct points will determine a cubic function.
P(x) is the degree 3 polynomial through the 4 points, a standard way to write it is
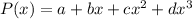
Next replace the given points one by one, which leads to a system of 4 equations and 4 variables (namely a,b,c,d)
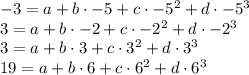
We can rewrite this system as follows:
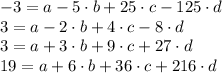
To use the Gaussian Elimination we need to express the system of linear equations in matrix form (the matrix equation Ax=b).
The coefficient matrix (A) for the above system is
![\left[\begin{array}{cccc}1&-5&25&-125\\1&-2&4&-8\\1&3&9&27\\1&6&36&216\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/qecmnlqilk6w52zhdjymqyo47sqdaolhbl.png)
the variable matrix (x) is
![\left[\begin{array}{c}a&b&c&d\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/no0w2mnawtvzh9b6dh12774cv8m1vxcdxj.png)
and the constant matrix (b) is
![\left[\begin{array}{c}-3&3&3&19\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/l0oieiv8c9sot72tvthiqpwqdl178hbdhq.png)
We also need the augmented matrix, it is obtained by appending the columns of the coefficient matrix and the constant matrix.
![\left[\begin{array}c1&-5&25&-125&-3\\1&-2&4&-8&3\\1&3&9&27&3\\1&6&36&216&19\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/n4xdtpzvvffc358res2o8puofe86djfpzf.png)
To transform the augmented matrix to the reduced row echelon form we need to follow these steps:
- Subtract row 1 from row 2
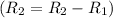
![\left[\begin{array}c1&-5&25&-125&-3\\0&3&-21&117&6\\1&3&9&27&3\\1&6&36&216&19\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/jjbepdsd5e837kjf1anonf5eucoexqagma.png)
- Subtract row 1 from row 3
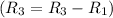
![\left[\begin{array}cccc1&-5&25&-125&-3\\0&3&-21&117&6\\0&8&-16&152&6\\1&6&36&216&19\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/xqtdtx8tzsc4mszsi11yqv2332mr01dm7y.png)
- Subtract row 1 from row 4
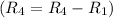
![\left[\begin{array}c1&-5&25&-125&-3\\0&3&-21&117&6\\0&8&-16&152&6\\0&11&11&341&22\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/rml8i3dcn744ad61ocjm6969w9le7zlvan.png)
- Divide row 2 by 3
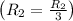
![\left[\begin{array}c1&-5&25&-125&-3\\0&1&-7&39&2\\0&8&-16&152&6\\0&11&11&341&22\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/qat7yueuh2yvj7ea8imngl8hhmcpqtw20n.png)
- Add row 2 multiplied by 5 to row 1
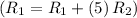
![\left[\begin{array}c1&0&-10&-70&7\\0&1&-7&39&2\\0&8&-16&152&6\\0&11&11&341&22\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/n9mmtp89h45ij9234xk0wwg0fs91odl14i.png)
- Subtract row 2 multiplied by 8 from row 3
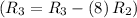
![\left[\begin{array}cccc1&0&-10&-70&7\\0&1&-7&39&2\\0&0&40&-160&-10\\0&11&11&341&22\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/beuxw3f2o3or8c5aj7f0vu88b4g01uqabt.png)
- Subtract row 2 multiplied by 11 from row 4
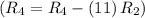
![\left[\begin{array}c1&0&-10&-70&7\\0&1&-7&39&2\\0&0&40&-160&-10\\0&0&88&-88&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/f9brex2ai7ognz3oqicez1n4o9s9911o9s.png)
- Divide row 3 by 40
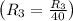
![\left[\begin{array}cccc1&0&-10&-70&7\\0&1&-7&39&2\\0&0&1&-4&-1/4\\0&0&88&-88&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/oyvex30vv4enzjikujh44nf8vqx0n6vej5.png)
- Add row 3 multiplied by 10 to row 1
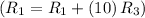
![\left[\begin{array}cccc1&0&0&30&9/2\\0&1&-7&39&2\\0&0&1&-4&-1/4\\0&0&88&-88&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/ku5xxmpntxpz7gi5h9ke5awwe8gz5ssahk.png)
- Add row 3 multiplied by 7 to row 2
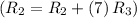
![\left[\begin{array}cccc1&0&0&30&9/2\\0&1&0&11&1/4\\0&0&1&-4&-1/4\\0&0&88&-88&0\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/xujdpx98mplabf995bz1xjcqhy6njraals.png)
- Subtract row 3 multiplied by 88 from row 4
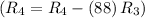
![\left[\begin{array}c1&0&0&30&9/2\\0&1&0&11&1/4\\0&0&1&-4&-1/4\\0&0&0&264&22\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/b4ozzhrwcvse0oke3ym9i7tfdyyx7zgq2y.png)
- Divide row 4 by 264
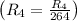
![\left[\begin{array}cccc1&0&0&30&9/2\\0&1&0&11&1/4\\0&0&1&-4&-1/4\\0&0&0&1&1/12\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/d0ckjhss5i93sjnbe8q32e5iymlt5rjy51.png)
- Subtract row 4 multiplied by 30 from row 1
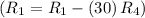
![\left[\begin{array}c1&0&0&0&2\\0&1&0&11&1/4\\0&0&1&-4&-1/4\\0&0&0&1&1/12\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/4f4km7u0cl33i418ui53ueu5axb2mf297n.png)
- Subtract row 4 multiplied by 11 from row 2
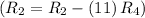
![\left[\begin{array}c1&0&0&0&2\\0&1&0&0&-2/3\\0&0&1&-4&-1/4\\0&0&0&1&1/12\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/tbghbppsj41rb3mu29wz5e6y1gg5rkmbbw.png)
- Add row 4 multiplied by 4 to row 3
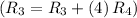
![\left[\begin{array}c1&0&0&0&2\\0&1&0&0&-2/3\\0&0&1&0&1/12\\0&0&0&1&1/12\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/epp4cqdv02ja1amwg0p58y5reod4blnq0h.png)
From the reduced row-echelon form the solutions are:
![\left[\begin{array}{c}a=2&b=-2/3&c=1/12&d=1/12\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/9a9txaihqdpm6pjcchsh1kgsyy9nh0mogt.png)
The polynomial P(x) is:
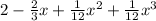
We can check our solution plotting the polynomial and checking that it passes through the points.