Answer:
a) The student has to run for 8.9 s.
b) The student has to run for 47 m.
c) The bus is traveling at 1.5 m/s when the student reaches the bus.
d) No, she will not catch the bus running at 2.00 m/s.
e) The minimum speed the student must have to catch the bus is 3.7 m/s.
f) The student has to run for 21.3 s if she runs at 3.7 m/s to catch the bus.
g) She has to run 79 m to catch the bus running at 3.7 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The equations for a straight movement are:
With constant acceleration:
x = x0 + v0 * t + 1/2 * a * t²
v = v0 + a *t
With constant velocity (a = 0):
x = x0 + v * t
Where
x = position at time t
x0 = initial position
v0 = initial velocity
v = velocity
a = acceleration
t = time
a) When the student catches the bus, the position of the bus and the student are the same:
x student = x bus
The student moves with constant speed while the bus has a constant acceleration. If the origin of the reference system is located where the student starts running, then, x0 student = 0 and x0 bus = 40.7 m. Since the bus starts from rest, v0 = 0.
x student = v * t
x bus = x0 + v0 * t + 1/2 * a * t² = x0 + 1/2 * a * t²
x student = x bus
v * t = x0 + 1/2 * a * t²
Replacing with data:
5.3 m/s * t = 40.7 m + 1/2 (0.168 m/s²) * t²
0 = 40. 7 m - 5.3 m/s * t + 0.084 m/s²¨* t²
Solving the quadratic equation:
t = 8.9 s and t = 54.1 s
We discard the higher value because if the student catches the bus at 8.9 s, she will not catch it again at 54.1 s.
The student has to run for 8.9 s.
b) Using the equation for position of the student:
x = v * t = 5.3 m/s * 8.9 s =47 m
The student has to run for 47 m
c) Using the equation for velocity of the bus:
v = v0 + a * t = 0 m/s + 0.168 m/s² * 8.9 s
v = 1.5 m/s
The bus is traveling at 1.5 m/s when the student reaches the bus
d) The quadratic equation after equalizing the position of the student and the position of the bus would be:
0 = 40. 7 m - 2 m/s * t + 0.084 m/s²¨* t²
If we solve this using the formula to obtain the roots of the parabola we will obtain:
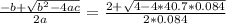
Since the term
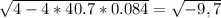 is not defined in the real numbers, there is no "t" such as the equation of the parabola equals 0. The parabola has no roots. Then, the student will not catch the bus if she runs at 2.00 m/s.
is not defined in the real numbers, there is no "t" such as the equation of the parabola equals 0. The parabola has no roots. Then, the student will not catch the bus if she runs at 2.00 m/s.
e) The term inside the square root in
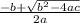
has to be positive or 0, then:
b² - 4* a* c ≥ 0
Notice that "b" is the speed at which the student runs, "a" is 0.084 and "c" is 40. 7 ( see the equation of the parabola obtained in a)). Then:
b² ≥ 4 * a * c
b ≥ √ 4 * a * c
b ≥ √ 4 * 0.084 * 40.7
b ≥ 3.7 m/s
The minimum speed the student must have to catch the bus is 3.7 m/s.
f) Now we have to solve the quadratic equation obtained in a), but using -3.7 as value of "b". Solving the quadratic equation, we will obtain the values of t = 21.3 s and 22.7 s. Again, we discard the higher value.
The student has to run for 21.3 s if she runs at 3.7 m/s to catch the bus.
g) The distance is given by the equation for the position of the student:
x = v * t = 3.7 m/s * 21.3 s = 79 m.
She has to run 79 m to catch the bus.