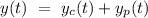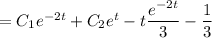Answer:
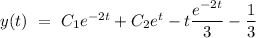
Explanation:
As given in question, we have to find the solution of differential equation
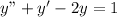
by using the variation in parameter method.
From the above equation, the characteristics equation can be given by
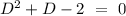
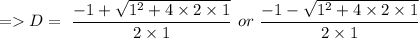
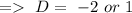
Since, the roots of characteristics equation are real and distinct, so the complementary function of the differential equation can be by
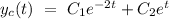
Let's assume that
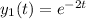
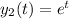
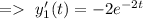
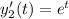
and g(t)=1
Now, the Wronskian can be given by
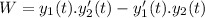

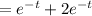
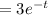
Now, the particular solution can be given by
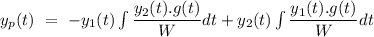
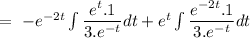
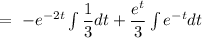
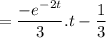
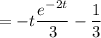
Now, the complete solution of the given differential equation can be given by