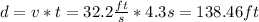Answer:
138.46 ft
Step-by-step explanation:
When the ball is dropped until the moment it hits the water, the ball moves in a uniform acceleration motion. Therefore, the equation that describes the movement of the ball is:
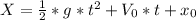
Where X is the distance that the ball has fallen at a time t.
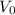 is the initial velocity, which is 0 ft/s as the ball was simply dropped.
is the initial velocity, which is 0 ft/s as the ball was simply dropped.
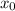 is the initial position, we will say that this value is 0 in the position where the ball was dropped for simplicity, and it increases as the ball is falling. Now, we replace x with 16 feets and solves for t:
is the initial position, we will say that this value is 0 in the position where the ball was dropped for simplicity, and it increases as the ball is falling. Now, we replace x with 16 feets and solves for t:
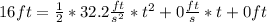
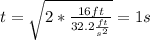
The velocity that the ball will have at the moment the ball that the ball hits the water will be:
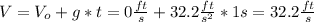
The time that will take the ball to reach the bottom from the top of the lake will be t = 5.3s - 1s = 4.3s. And as the ball will travel with constant velocity equal to 32.2 ft/s^2, the depth of the lake will be: