Answer:
![y(x)\ =\ √(x)[C_1cos(√(3))/(2)logx+C_2sin(√(3))/(2)logx]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/kzz7mv4ujpc5r5urztekq3pps3rfffakpr.png)
Explanation:
Given differential equation is
 (1)
(1)
Let's assume that
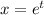
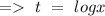
then,
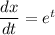
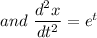
We can write,
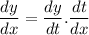
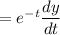
Similarly,
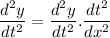
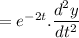
Putting these values in equation (1), we will get
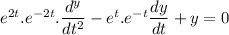
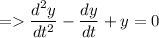
So, the characteristics equation can be given as
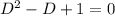
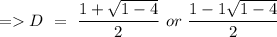
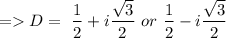
Hence, the general solution of the equation can be give by
![y(t)\ =\ e^{(t)/(2)}[C_1cos(√(3))/(2)t+C_2sin(√(3))/(2)t]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/5lsuaqz1igq1c5t1s8mha991nikr4u3298.png)
Now, by putting the value of t in above solution, we will have
![y(x)\ =\ e^{(1)/(2)logx}[C_1cos(√(3))/(2)logx+C_2sin(√(3))/(2)logx]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/s1h3pf532091ty9ah5hgb4bgt6nonio1tm.png)
![y(x)=\ √(x)[C_1cos(√(3))/(2)logx+C_2sin(√(3))/(2)logx]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/k7la5h37soyhd37ghx4omyw4by6ilyagzu.png)
Hence, the solution of above given differential equation can be given by
![y(x)=\ √(x)[C_1cos(√(3))/(2)logx+C_2sin(√(3))/(2)logx]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/k7la5h37soyhd37ghx4omyw4by6ilyagzu.png)