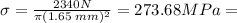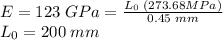Answer:
maximum length of the specimen before deformation = 200 mm
Step-by-step explanation:
Hi!
If we have a cylinder with length L₀ , and it is elasticaly deformed ΔL (so the final length is L₀ + ΔL), the strain is defined as:
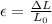
And the tensile stress is:
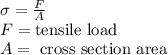
Elastic modulus E is defined as:
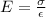
In this case ΔL = 0.45 mm and we must find maximum L₀. We know that A=π*r², r=(3.3/2) mm. Then: