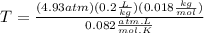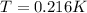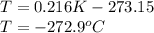Answer:
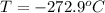
Step-by-step explanation:
We have the ideal gasses equation
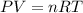 and the expression for the specific volume
and the expression for the specific volume
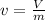 , that is the inverse of the density, and for definition the number of moles is equal to the mass over the molar mass, that is
, that is the inverse of the density, and for definition the number of moles is equal to the mass over the molar mass, that is
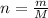
And we can relate the three equations as follows:
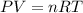
Replacing the expression for n, we have:
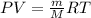
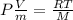
Replacing the expression for v, we have:
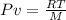
Now resolving for T, we have:
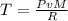
Now, we should convert all the quantities to the same units:
-Convert 500kPa to atm
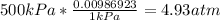
-Convert 0.2
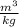 to
to
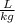
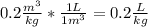
- Convert the molar mass M of the water from
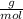 to
to
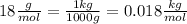
Finally we can replace the values: