Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
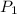 = 2.34 kPa = 2.34 \times 1000 Pa = 2340 Pa = 0.0231 atm
= 2.34 kPa = 2.34 \times 1000 Pa = 2340 Pa = 0.0231 atm
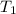 = (20 + 273) K = 293 K
= (20 + 273) K = 293 K
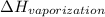 = 2537.4 kJ/kg = 2537400 J/kg
= 2537.4 kJ/kg = 2537400 J/kg
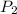 = ?,
= ?,
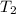 = (40 + 273) K = 313 K
= (40 + 273) K = 313 K
According to Clausius-Clapeyron equation,
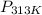 =
=
![P_(293) Exp[(-\Delta H_(v))/(R) ((1)/(313) - (1)/(293))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ijw2egg896bpdu5nsqpfz60cellejcdlxf.png)
=
![0.0213 Exp [(-2537400 J/kg)/(8.314 J/mol) ((1)/(313) - (1)/(293))K]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pqxu3y80x2in3iswxy8t4819tzwlmi6oi5.png)
=
 atm
atm
or, = 18846.45 kPa
Thus, we can conclude that the vapor pressure at
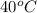 is 18846.45 kPa.
is 18846.45 kPa.