Answer:
[HI] = 0,0264 M
[H₂] = 0,003299 M
[I₂] = 0,003299 M
Step-by-step explanation:
For the equation:
2 HI (g) ⇄ H₂(g) + I₂(g) With k= 0,0156. Also, k=
![([H_(2)[I_(2) ] )/([HI]^(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ft206ntypidutjmiv5qkc9vks953mldb4z.png) (1)
(1)
The initial concentration of HI is:
[HI] =
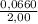 = 0,0330 M
= 0,0330 M
The concentration of the reactant and products in equilibrium is:
[HI] = 0,033 M - 2x ⇒ because 2 moles are consumed
[H₂] = x ⇒ because 1 mole is produced
[I₂] = x ⇒ Also, 1 mole is produced
Thus, replacing in (1):
0.0156 =
![([x]^2)/([0,0330-2x]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/5wrjwv793msj6zxb3uop2tfi7ikmssmo2w.png)
The quadratic equation to solve is:
0,9376x² + 0,0020592x - 0,000017 = 0
Have two solutions:
x = -0,0054955 ⇒ No physical sense. Will produce negative concentrations
x = 0,003299⇒ Real answer
Thus, concentrations in equilibrium are:
[HI] = 0,033 - 2×0,003299 = 0,0264 M
[H₂] = 0,003299 M
[I₂] = 0,003299 M
I hope it helps!