Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given parameters:
Molar mass of compound = 60.1g/mol
Mass of fuel used in the combustion process = 2.859g
Mass of carbon dioxide produced = 4.190g
Mass of oxygen produced= 3.428g
Unknown parameters;
Empirical and molecular formula of the compound
Solution
The empirical formula of a compound is its simplest formula. The molecular formula is the actual formula of the compound showing the proportions of the atoms.
We can derive the empirical formula of a compound from its molecular formula and vice versa.
Here, we have to work from empirical formula to molecular formula.
Solving
- We know that the compound contains C, H and N atoms. We need to first find the masses of these atoms in the compound
For Carbon, we can determine the mass from the amount of carbon dioxide produced:
mass of carbon in compound =
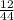 x 4.19g = 1.14g
x 4.19g = 1.14g
For Hydrogen, we can determine the mass from the amount of water produced:
mass of hydrogen in compound =
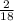 x 3.428g = 0.38g
x 3.428g = 0.38g
To determine the mass of N in the compound:
mass of compound = mass of C + mass of H + mass of N
mass of N = mass of compound - (mass of C + mass of H)
mass of N = 2.859g - (1.14g + 0.38g) = 1.34g
2. we now proceed to find the empirical formula using the process below:
Elements C H N
mass of the
elements 1.14 0.38 1.34
Atomic mass
of elements 12 1 14
Number of
moles 1.14/12 0.38/1 1.34/14
0.095 0.38 0.095
Dividing by
the smallest 0.095/0.095 0.38/0.095 0.095/0.095
1 4 1
The empirical formula of the compound is CH₄N
To obtain the molecular formula, we need to find the number of times the empirical formula must have repeated itself in the original form.
Molar mass of CH₄N = 12 + 4 + 14 = 30g/mol
Ratio =
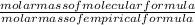 =
=
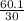 = 2
= 2
Molecular formula = 2(CH₄N) = C₂H₈N₂