Answer: Option (d) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Tube diameter d = 10 mm = 0.01 m
Velocity of glycerol, v = 0.5 m/s
Density of glycerol (
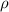 ) = 1240 kg/m3
) = 1240 kg/m3
Dynamic viscosity of glycerol (
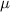 ) = 0.0813 pa.s
) = 0.0813 pa.s
Reynolds number (Re) =
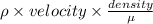
=

= 76.26
Therefore, according to Reynolds number we can say that flow is laminar.
Lt =
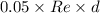
=
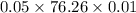
=
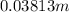
As it is known that 1 m = 1000 mm. Hence, in 0.03813 m will be equal to

= 38.13 mm
Thus, we can conclude that the transition length of glycerol is 38.13 mm.