Answer:
Head loss in turbulent flow is varying as square of velocity.
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that head loss in turbulent flow given as
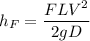
Where
F is the friction factor.
L is the length of pipe
V is the flow velocity
D is the diameter of pipe.
So from above equation we can say that
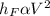
It means that head loss in turbulent flow is varying as square of velocity.
We know that loss in flow are of two types
1.Major loss :Due to surface property of pipe
2.Minor loss :Due to change in momentum of fluid.